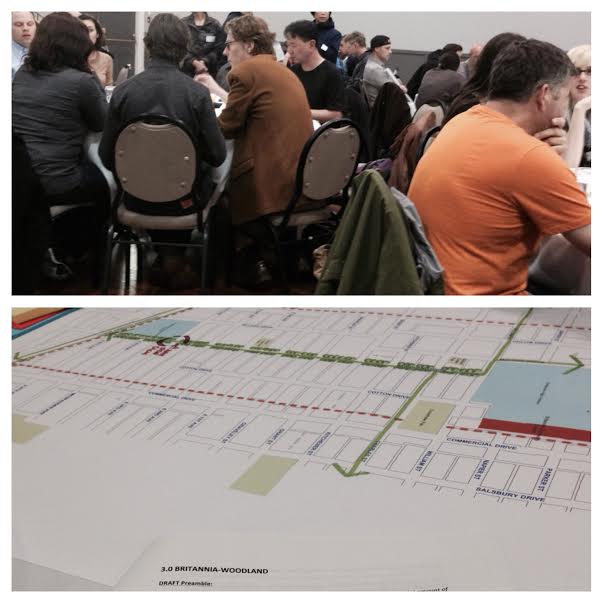
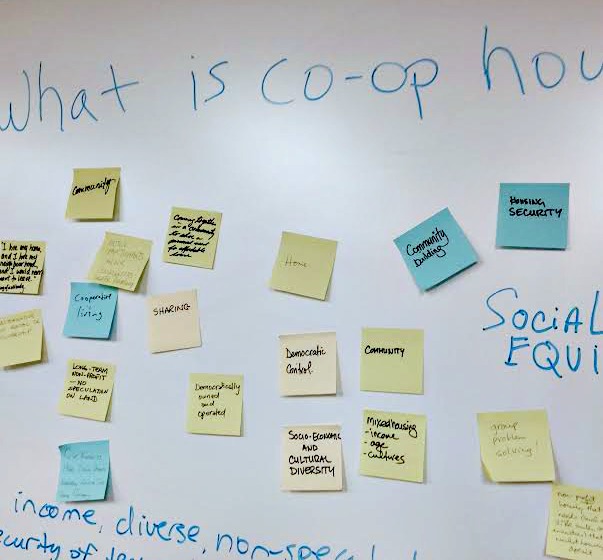Tonight, the Citizens’ Assembly on the Grandview-Woodland Community Plan had its last community roundtable. The subject of discussion was the draft sub-area recommendations, on specific parts of the community like Cedar Cove, Nanaimo, and Broadway and Commercial.
I arrived shortly before seven and the line up of participants was nearly out the door, while inside, most of the tables were almost full. I managed to get a seat at one of the Britannia-Woodland discussion tables, then during the second round, sat at a Commercial Drive discussion table. People were still arriving as the discussion started and as with all of the meetings I’ve attended so far, there were enough participants to fill at least a half dozen more tables. As it was, people found space where they could, or sat two-deep for some of the more contentious discussions.

As always, I was impressed by the knowledge and commitment of the Assembly members and the community members who came to the meeting. There were fruitful discussions and agreement on many issues, though there will never be consensus on others.
Here are a few of the highlights from the summaries at the end of the night:
- More creative use of industrial lands is needed.
- Nanaimo Street needs to be developed, but in a way that respects current residential uses.
- Affordable housing is the crucial issue for the Britannia-Woodland sub-area.
- Cedar Cove needs to be better integrated into the neighbourhood, with transit and Commercial Drive-like spaces for small business.
- Commercial Drive needs to be kept affordable for independent, small-scale businesses. Ideas like allowing businesses to make use of laneways might be part of the solution.
- Public space needs to be truly public, rather that the private-public space seen in places like Yaletown, that’s not truly accessible to citizens.
- Co-operative housing and other affordable housing need to be protected and promoted, so that we can retain a mixed income community.
No consensus was reached on the development at Venables and Commercial and there was also a concern that though there has been broad consensus at all public meetings on a height restriction of four storeys, the proposals that are presented to the public keep integrating greater height limits.
There was broad support, with some objections, to the plan for bike lanes along Commercial/Salsbury, along with wider sidewalks from 1st to Broadway. The active transportation plan for Commercial seems like it’s going to become a reality.
There’s a divide of opinion on how to protect and expand affordable housing in the neighbourhood. Some believe that density created through condo development and tower construction will achieve that, though the results elsewhere in the City show the opposite effect. Others (including me) believe that density achieved through infill, smaller development, and more distributed density will help protect existing affordable housing stock, while allowing more to be built. Creative approaches to preserving existing buildings, while allowing redevelopment are seen as crucial by many of us.
Those are just a few of the points made tonight. And there’s still a little time to comment on the draft before the Assembly’s last meeting on May 9th. You can email them at assembly@grandview-woodland.ca and you can download a copy of the draft here.
I don’t hold out much hope that the City will respect the recommendations of the Assembly or the neighbourhood at large. But I still don’t think this process has been a waste of time. The Assembly has done an admirable job of recording the views of the neighbourhood and sifting through all the information that’s been given to them.
Most importantly, the overwhelming interest in the process shows just how active our neighbourhood will be in challenging the City if it should present us with something that doesn’t reflect the concerns and ideas that this community has voiced.